Floods are natural disasters that can cause widespread devastation, resulting in loss of life, property damage, and economic disruption. As the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events continue to rise, understanding and mitigating flood risks have become more critical than ever. One essential tool in this endeavour is a flood risk map. In this blog, we will explore what flood risk maps are, their significance, and how they aid in enhancing preparedness and resilience in flood-prone areas.
What is a Flood Risk Map?
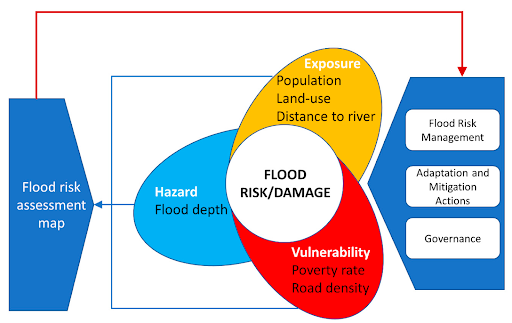
A flood risk map visually represents an area’s potential flood hazards and vulnerability. It combines various data sources, such as historical flood records, topography, rainfall patterns, river and coastal dynamics, and land use information. Using advanced geographic information system (GIS) technology, flood risk maps assign different zones to reflect varying levels of flood susceptibility, including high-risk, moderate-risk, and low-risk areas.
Significance of Flood Risk Maps
Flood risk maps serve multiple purposes and are indispensable tools for governments, urban planners, emergency management agencies, and communities.
- They raise awareness about flood-prone regions, allowing policymakers to develop effective strategies and allocate resources accordingly.
- They help homeowners, businesses, and individuals make informed decisions regarding property purchases, insurance coverage, and emergency planning.
- Flood risk maps facilitate early warning systems, evacuation planning, and the implementation of flood mitigation measures, ultimately reducing the impact of floods and saving lives.
Components of a Flood Risk Map:
- Floodplain boundaries:
Flood risk maps define the boundaries of floodplains, which are areas at high risk of inundation during a flood event. These boundaries help identify regions where floodwaters are likely to spread, allowing authorities to prioritise mitigation efforts and implement appropriate land-use regulations.
- Flood depths:
A crucial component of flood risk maps is the indication of flood depths. This information illustrates how deep the water could potentially get in different areas during a flood. It helps communities understand the severity of potential flooding and aids in decision-making related to infrastructure development, evacuation planning, and emergency response.
- Flood frequencies:
Flood risk maps incorporate data on flood frequencies, providing an estimate of the likelihood of flooding within a specific timeframe. This information helps assess the probability of different flood events occurring, ranging from minor floods to major catastrophic events. Understanding flood frequencies enables authorities to develop appropriate flood management strategies and allocate resources effectively.
- Critical infrastructure locations:
Flood risk maps often include the locations of critical infrastructure such as hospitals, power plants, transportation networks, and water treatment facilities. Identifying these vital assets on the map is crucial for disaster response and recovery planning. It helps emergency management agencies prioritise protection measures, evacuation routes, and contingency plans to ensure the continuity of essential services during and after a flood.
- Emergency evacuation routes:
In the event of a flood, timely evacuation is crucial for saving lives and minimising injuries. Flood risk maps include designated emergency evacuation routes, which guide residents and emergency personnel to safer areas. These routes are carefully planned to avoid flood-prone areas and ensure efficient evacuation during emergencies.
- Flood protection measures:
Flood risk maps may also highlight existing flood protection measures such as levees, flood walls, or stormwater management systems. These protective structures are indicated on the map to visually represent the infrastructure in place to mitigate flood risks. Identifying these measures helps authorities assess their effectiveness, plan for maintenance and upgrades, and identify areas where additional flood protection measures are necessary.
Enhancing Preparedness and Resilience
Flood risk maps play a crucial role in enhancing preparedness and building resilience in flood-prone regions. By identifying high-risk areas, communities can implement appropriate flood mitigation measures such as levees, flood walls, and stormwater management systems. These maps also inform emergency response planning, enabling authorities to allocate resources efficiently and evacuate vulnerable populations in a timely manner. Furthermore, flood risk analysis support the development of insurance policies and financial instruments that incentivise resilience-building activities. Ultimately, by utilising flood risk maps, communities can reduce the economic and human toll of flooding and improve their ability to bounce back after a disaster.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing flood risks is critical for creating resilient communities in an era of increasing climate change impacts. Flood risk maps provide essential information that enables governments, planners, and individuals to make informed decisions, implement appropriate mitigation measures, and improve emergency response strategies. By utilising these maps effectively, we can enhance preparedness, minimise damages, and save lives during flood events. As the frequency and severity of floods continue to rise, the significance of flood risk maps in building resilience cannot be overstated. Let us leverage this invaluable tool to create safer, more sustainable communities for the future.
You may also like
-
Classified Websites in India: A Digital Marketplace for All
-
Why Sod Installation is the Quickest Way to a Beautiful Lawn?
-
The Role of Statutes and Case Law in Policy Limit Access
-
Setting Up a Home Theater with LG CineBeam Q The Ultimate Guide
-
Business Listing Sites in USA: 2025 Guide for Better Online Visibility